Satisfaction Guaranteed
All products are handled with strict quality standards to ensure consistent research-grade excellence.
Secure Ordering
Our checkout is SSL encrypted and completely secure.
Third-party Tested
Our products are verified by independent third party laboratories to meet quality standards.
Batch & Lot Tracking
All product batches and lots are assigned unique identifiers and tied to publicly posted lab reports.
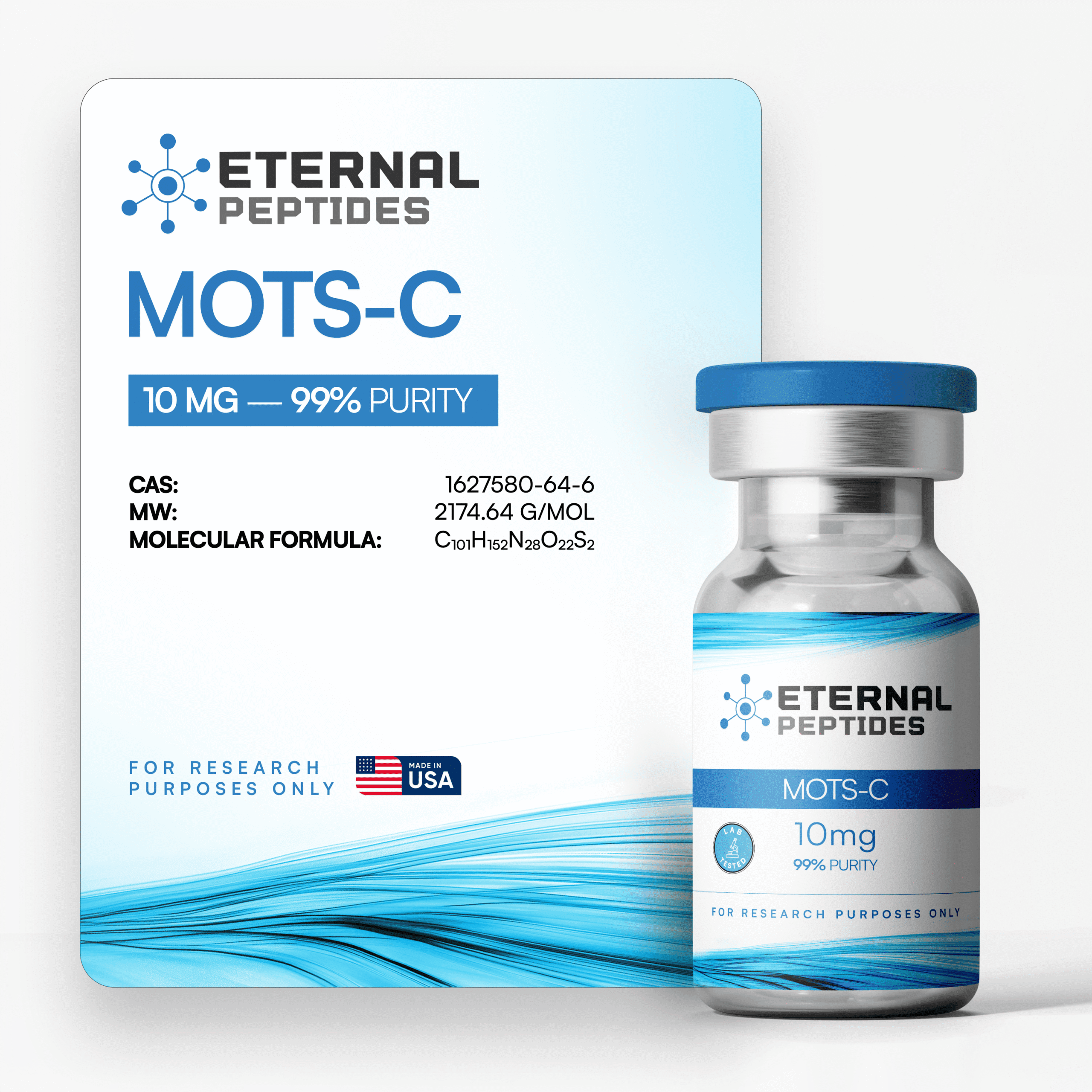
MOTS-C (10mg)
$65.00 Original price was: $65.00.$59.99Current price is: $59.99.
Save 5.01$ (8% Off)
Discount per Quantity
| Quantity | Discount | Price |
|---|---|---|
| 5 - 10 | 5% | $56.99 |
| 11 - 20 | 10% | $53.99 |
| 21+ | 15% | $50.99 |
Concentration: ≥99%
Rigorous Third-Party Testing
Every batch of our research chemicals and peptides undergoes third-party testing.
*Disclaimer: This product is intended solely for laboratory research purposes. It is not suitable for consumption by humans, nor for medical, veterinary, or household purposes. Kindly review our Terms & Conditions before making a purchase.

Always quality-tested, verified with third party COA’s
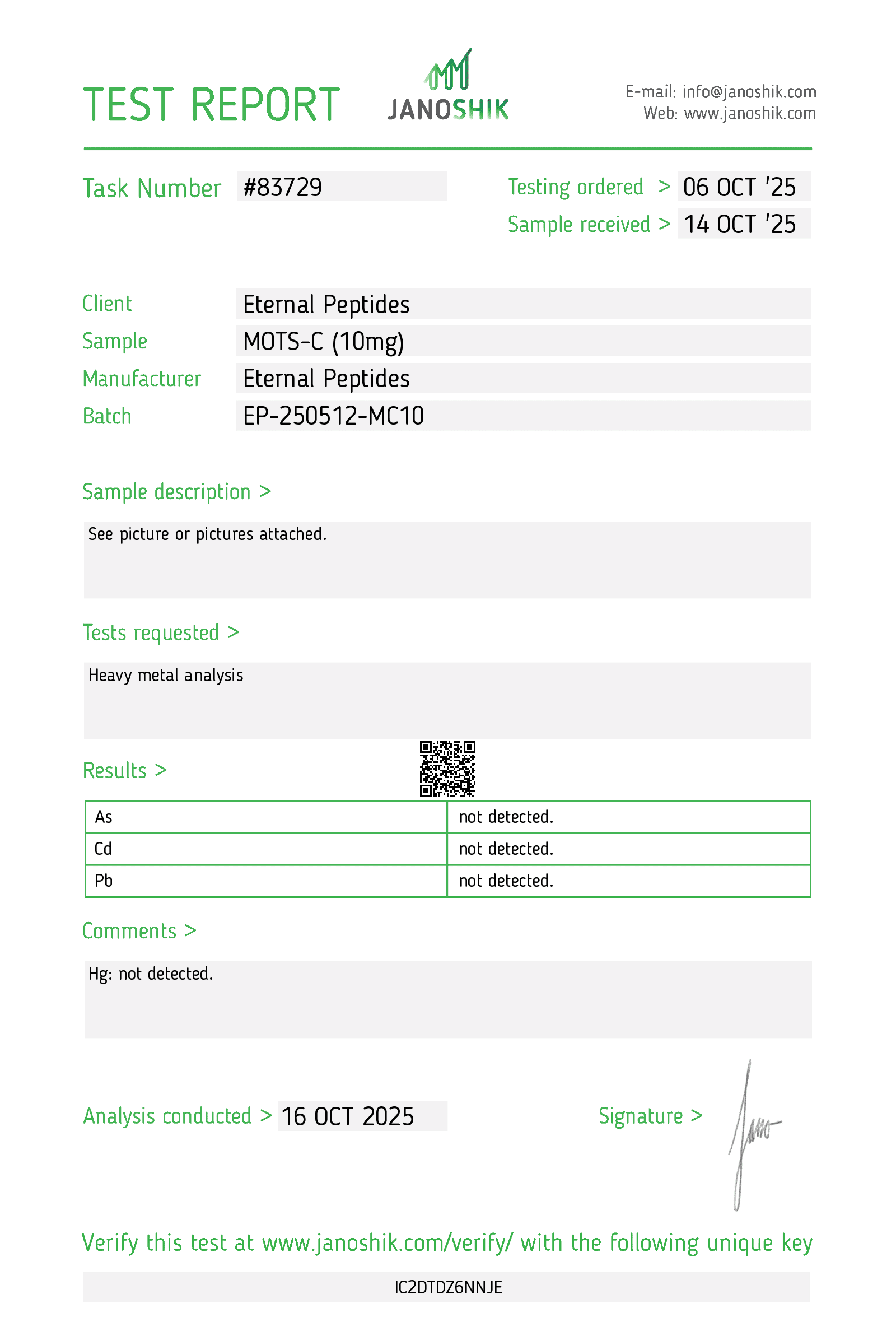
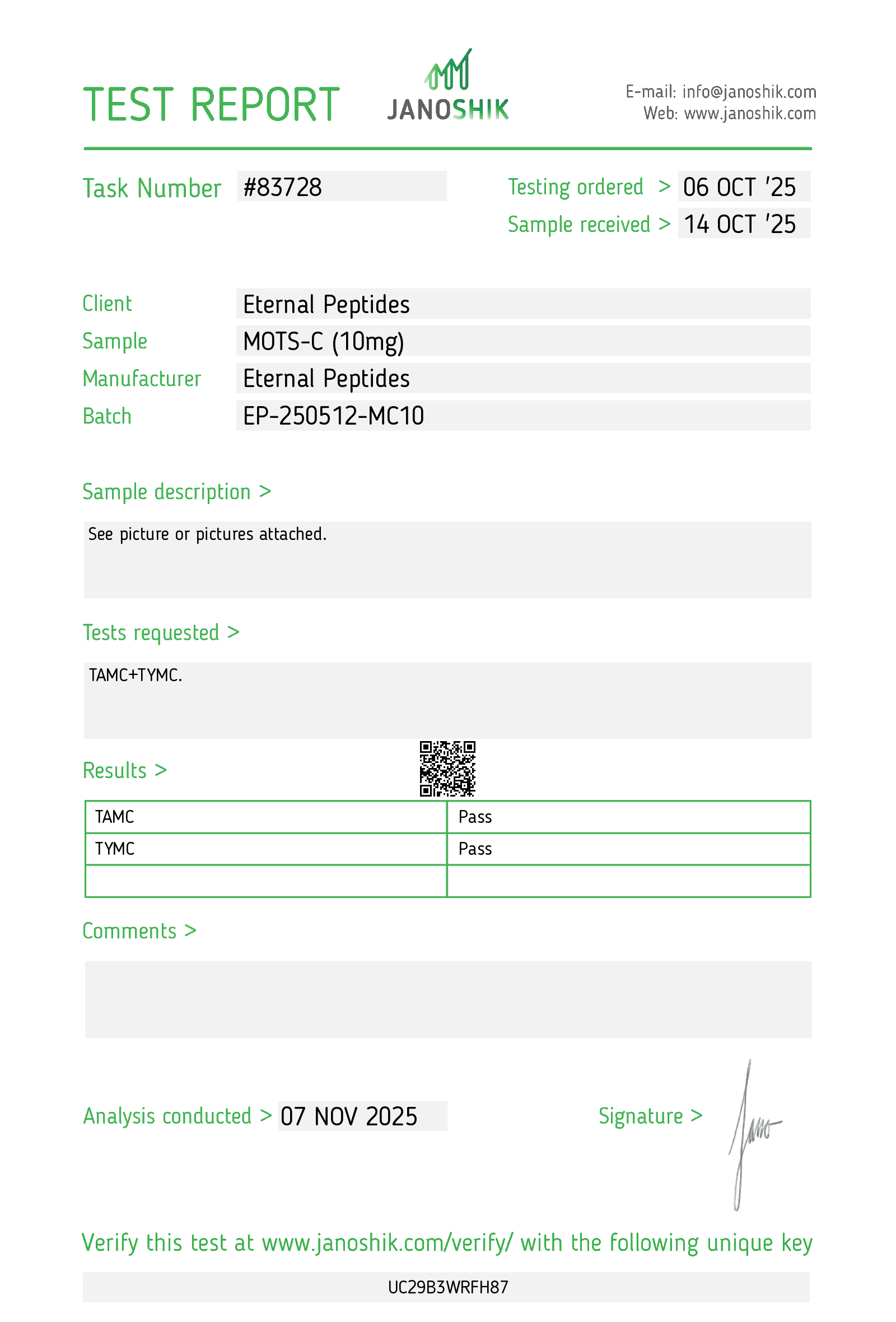
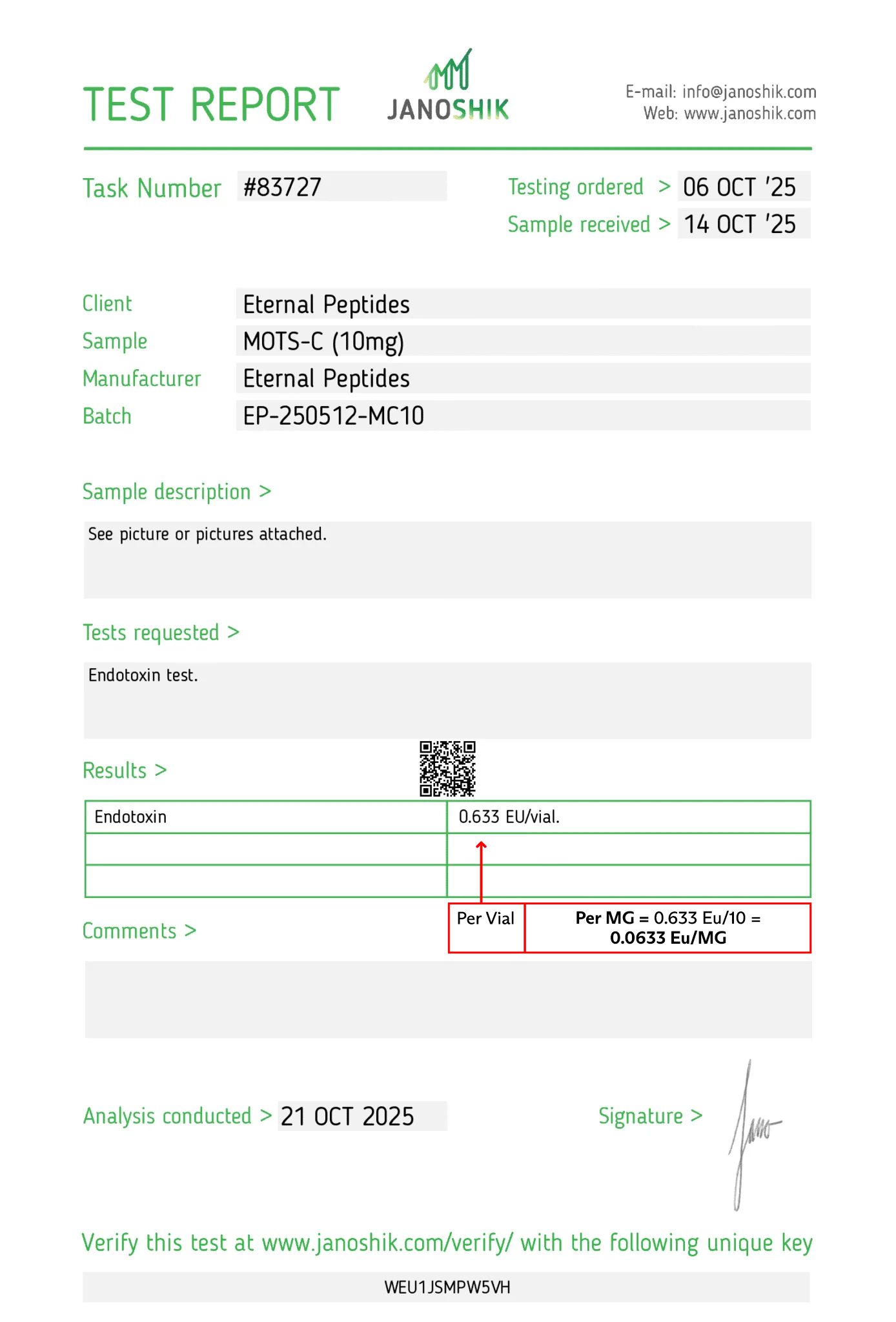
At every step, we prioritize quality by conducting rigorous third-party testing on all our products. These tests focus on five key characteristics- identity, purity, sterility, and endotoxin levels, and heavy metal content-ensuring that each product meets the highest standards of quality with independent third-party Certificates of Analysis (COAS) to verify our commitment to excellence.
Identity Test
Purity Test
Sterility Test
Endotoxin Test
Heavy Metals Test
Identity Test
Purity Test
Sterility Test
Endotoxin Test
Heavy Metals Test
*Disclaimer: This product is intended solely for laboratory research purposes. It is not suitable for consumption by humans, nor for medical, veterinary, or household purposes.Kindly review our Terms & Conditions before making a purchase.
Shop high-purity MOTS-C 10mg at Eternal Peptides, the trusted source for verified research compounds in the USA. This mitochondrial-derived peptide is synthesized to a standard of ≥99% purity, with every batch rigorously tested and certified by Janoshik Analytical. MOTS-C is a primary reagent for researchers investigating AMPK activation, cellular energy regulation, and metabolic flexibility. Order today for fast, secure US shipping and free Priority delivery on all orders over $200.
What is MOTS-C?
MOTS-C (Mitochondrial Open Reading Frame of the 12S rRNA-C) is a short, mitochondria-derived peptide classified as a member of the mitochondrial-derived peptides (MDPs). It is composed of a small amino acid sequence encoded within mitochondrial DNA rather than the nuclear genome, distinguishing it structurally and functionally from most conventional signaling peptides.
In other words, MOTS-C is a synthetic research analogue of an endogenously expressed mitochondrial peptide identified through genomic analysis of mitochondrial open reading frames.
In the scientific literature, MOTS-C is primarily investigated for its role in mitochondrial signaling, cellular metabolism, and adaptive energy regulation. Preclinical research has explored its involvement in metabolic stress responses, insulin sensitivity, and exercise-related signaling, with most findings originating from in vitro models and animal studies.
Mechanistically, MOTS-C is associated with modulation of metabolic pathways linked to glucose utilization, fatty acid oxidation, and cellular stress adaptation, potentially through nuclear-mitochondrial signaling interactions. Since controlled human clinical data remains limited, these findings should be interpreted strictly within a preclinical research context.
How MOTS-C Works (Mechanism of Action)
MOTS-C is a pleiotropic, mitochondria-derived peptide studied primarily for its role in metabolic regulation and cellular stress adaptation[1]. Current mechanistic understanding comes largely from in vitro systems and animal models, where MOTS-C appears to influence multiple signaling pathways linked to energy balance, mitochondrial function, and cellular resilience.
AMPK Activation and Energy Sensing
One of the most consistently reported mechanisms of MOTS-C involves activation of AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK), a central regulator of cellular energy status. In preclinical studies, MOTS-C increases AMPK signaling in metabolically active tissues, particularly skeletal muscle. This pathway is frequently studied alongside NAD+ for its role in cellular energy metabolism. This activation promotes glucose uptake and shifts cells toward more efficient energy utilization during metabolic stress.
AMPK signaling is critical for maintaining cellular homeostasis when energy demand exceeds supply. By enhancing this pathway, MOTS-C is thought to help cells adapt to energetic challenges, which is relevant in research models examining metabolic strain or nutrient imbalance.
Regulation of Glucose Metabolism and Insulin Sensitivity
MOTS-C has been shown in animal models to influence glucose metabolism by improving insulin sensitivity and enhancing glucose clearance from circulation[1]. These effects are linked to downstream AMPK signaling and altered expression of genes involved in glucose transport and utilization.
In research settings, these metabolic changes are of interest because impaired glucose handling is a hallmark of metabolic dysfunction. MOTS-C’s ability to modulate these processes helps explain why it is frequently studied in models of diet-induced metabolic stress rather than acute tissue repair.
Nuclear Translocation and Gene Expression Modulation
Under conditions of metabolic or oxidative stress, MOTS-C has been observed to translocate from the mitochondria to the nucleus[3]. Once in the nucleus, it appears to interact with stress-responsive transcriptional programs, altering the expression of genes involved in metabolism and cellular defense.
This mitochondrial-to-nuclear signaling highlights a broader role for MOTS-C as a communication molecule rather than a single-pathway effector. In research contexts, this mechanism matters because it suggests MOTS-C can coordinate adaptive responses across cellular compartments.
Interaction With the Folate–Methionine Cycle
Preclinical studies suggest MOTS-C may influence the folate–methionine cycle, a metabolic pathway closely tied to amino acid balance and cellular redox state[4]. By modulating this cycle, MOTS-C indirectly affects availability of metabolic intermediates required for stress adaptation and energy regulation.
This mechanism is particularly relevant in experimental models examining nutrient sensing and metabolic flexibility. It reinforces the view of MOTS-C as a regulator of metabolic networks rather than a direct growth or repair signal.
Exercise-Mimetic and Stress Adaptation Effects
In animal models, MOTS-C administration has been associated with molecular changes similar to those observed during physical exercise, including enhanced mitochondrial efficiency and improved metabolic flexibility. These findings have led researchers to describe MOTS-C as having “exercise-mimetic” properties at the signaling level.
From a research standpoint, this mechanism is important for studying how cells adapt to repeated energetic demand. However, these effects remain preclinical, and their relevance to controlled human outcomes has not been firmly established.
MOTS-C Peptide Research Value
MOTS-c is studied in research as a mitochondria-derived signaling peptide involved in metabolic regulation and cellular stress responses. In simplified terms, laboratory models use MOTS-c to understand how mitochondrial signals influence energy use, metabolic efficiency, and physical performance at the cellular level.
Key areas of research value include:
- Studying metabolic flexibility, often described as how efficiently cells switch between using glucose and fat for energy
- Exploring insulin sensitivity and glucose handling, relevant to research on metabolic balance and energy regulation
- Investigating exercise and physical performance signaling, including how cells adapt to increased energy demand
- Examining mitochondrial communication, focusing on how mitochondria send signals that influence whole-cell behavior
- Researching cellular stress resistance, particularly responses to metabolic or oxidative stress
- Modeling age-related metabolic changes, as MOTS-c levels and activity appear to shift with aging in preclinical studies
MOTS-C Peptide Characteristics
| Property | Description |
| Name | MOTS-C (Mitochondrial Open Reading Frame of the 12S rRNA-C), a mitochondria-derived signaling peptide |
| Sequence | MRWQEMGYIFYPRKRR |
| Length | 16 amino acids |
| Molecular Weight | ~2,117 Da (minor variation possible depending on salt form and analytical method) |
| Formats | Lyophilized peptide supplied in glass vials |
| Purity | ≥99% purity, verified with COAs |
| Solubility | Soluble in sterile water or buffered aqueous solutions |
Batch: EP-250512-MC10
Handling & Storage Guidelines — MOTS-C
Store lyophilized MOTS-C at -4°F to 39°F (-20°C to 4°C) in a dry environment, protected from light and moisture. For long-term storage, freezing at -4°F (-20°C) is recommended. Upon reconstitution, use sterile water or an appropriate laboratory-grade buffer, allowing the solution to dissolve gently without vigorous agitation.
For the best stability, purity, and consistent results, purchase bacteriostatic water with your MOTS-C order.
Once reconstituted, aliquot working solutions into sterile containers to minimize repeated freeze–thaw cycles, which may compromise peptide integrity. Reconstituted solutions may be stored short term at 36°F–46°F (2°C–8°C) for up to several days, or frozen at -4°F (-20°C) for longer-term use.
Follow standard laboratory safety procedures and institutional handling protocols at all times.
COA / Quality Assurance — MOTS-C
Every batch of MOTS C supplied by Eternal Peptides is accompanied by a lot-specific Certificate of Analysis (COA) to support transparency, traceability, and reproducibility. COAs are produced after rigorous testing by third-party laboratories, including the leading Janoshik Analyticals, and all test results are accessible on our lab tests page.
CoAs typically document peptide identity confirmed by HPLC and/or mass spectrometry, purity (≥99%), and, where applicable, sterility and endotoxin testing results. They also include batch identifiers, allowing you to match analytical data precisely to the product received. This quality assurance framework supports audit readiness and consistent experimental outcomes.
Legal / Regulatory Disclaimer — MOTS-C
Eternal Peptides supplies MOTS-C strictly for laboratory research use only. It is not approved for human or veterinary use and must not be used for clinical administration, therapeutic purposes, diagnostic procedures, or consumption of any kind. The safety, efficacy, and pharmacological profile of MOTS C in humans have not been established.
You, as the purchaser, are solely responsible for ensuring compliance with all applicable local laws, institutional biosafety requirements, and research-use regulations. Any misrepresentation of intended use may result in regulatory or legal consequences. Eternal Peptides assumes no liability for misuse outside of approved research contexts.
Scientific References
- Zheng Y, Wei Z, Wang T. MOTS-c: A promising mitochondrial-derived peptide for therapeutic exploitation. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023 Jan 25;14:1120533.
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC9905433/
- Lee C, Kim KH, Cohen P. MOTS-c: A novel mitochondrial-derived peptide regulating muscle and fat metabolism. Free Radic Biol Med. 2016 Nov;100:182-187.
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC5116416/
- Kim KH, Son JM, Benayoun BA, Lee C. The Mitochondrial-Encoded Peptide MOTS-c Translocates to the Nucleus to Regulate Nuclear Gene Expression in Response to Metabolic Stress. Cell Metab. 2018 Sep 4;28(3):516-524.e7.
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC6185997/
- Gao Y, Wei X, Wei P, Lu H, Zhong L, Tan J, Liu H, Liu Z. MOTS-c Functionally Prevents Metabolic Disorders. Metabolites. 2023 Jan 13;13(1):125.
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC9866798/
- Wan W, Zhang L, Lin Y, Rao X, Wang X, Hua F, Ying J. Mitochondria-derived peptide MOTS-c: effects and mechanisms related to stress, metabolism and aging. J Transl Med. 2023 Jan 20;21(1):36.
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC9854231/
About the Author:
Dr. Sony Sherpa, MBBS, MD
is a board-certified clinician with a background in emergency medicine and clinical practice. She specializes in medical research analysis, ensuring that product information is grounded in evidence-based medicine and strictly adheres to the latest scientific standards in peptide research and recovery.
Related products
-
NAD+ (500mg)
$75.00Original price was: $75.00.$69.99Current price is: $69.99. Purchase & earn 70 points!Add to cart -
Selank (5mg)
$40.00Original price was: $40.00.$34.99Current price is: $34.99. Purchase & earn 35 points!Add to cart -
GLP-3 (R) (10mg)
$120.00Original price was: $120.00.$99.99Current price is: $99.99. Purchase & earn 100 points!Add to cart -
CJC 1295 + Ipamorelin (No DAC) (5mg/5mg)
$90.00Original price was: $90.00.$84.99Current price is: $84.99. Purchase & earn 85 points!Add to cart